Thingiverse
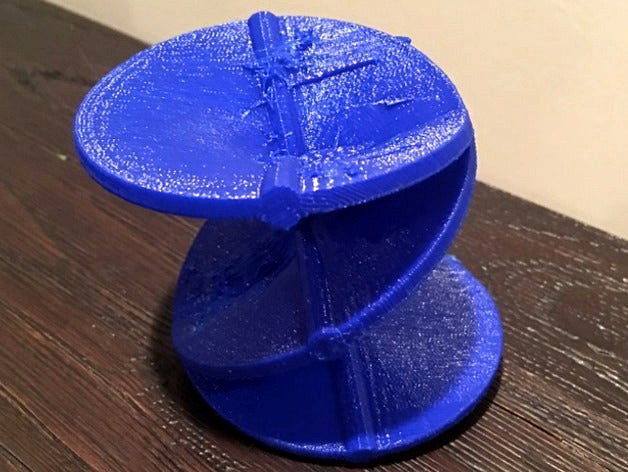

Riemann Surface of R^1/3 by Milton100
by Thingiverse
Last crawled date: 3 years ago
Object:
Riemann Surface of function f(z)= z^(1/3)
Created By:
Hope Roberts
Date, School & Place:
3/04/2016
George Mason University located in Fairfax, Va.
The creation took place in Mathematica for a class project for Math 493, Math Through 3D Printing.
Background of Riemann Surfaces
Riemann surfaces are named after Bernhard Riemann who was the first to study them.
Riemann surfaces are one way to show multi-valued functions. Showing that an element from the domain can map to multiple places in the codomain. They resemble surface like structures consisting of infinite sheets that are separated by vertical distance. They are configured in the complex plane, which has vectors 1, and i where i is imaginary and these vectors span the complex numbers. All complex numbers match to unique points in the complex plane. (mathworld). Another way to show the multi-valued functions is branch cuts, which is to take lines or line-segments of the multi-valued functions.
Representing a multivalued function is to ascribe not one point but instead infinite points to the domain. The sheets represented by the mappings from the origin and are all interconnected because it is undefined at the origin, which makes the origin, point not a part of the domain. The functions can be oriented in different ways by multiplying by the complex number.
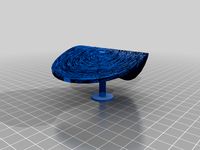
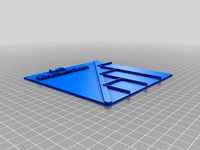
My function used for the Riemann surface was z^(1/3) and the surface was mapped using polar coordinates with the branches of the surface the tubes on top.
The branches also called branch cuts that are on my surface representing where the function is not continuous and is also non differentiable. The branches show when a sheet of the surface connects another sheet of the surface, which can be seen by the changing colors in surface in the mathematica code. As you increased distance in the polar coordinates you continue crossing branch cuts where the sheets are meeting. This is seen in my code and in my print represented by the tube overlay.
The second picture shows the surface without the tube overlay.
The third picture shows the tubes separate.
The fourth shows the combination.
And the final picture shows the stl file loaded onto MakerBot.
Riemann Surface of function f(z)= z^(1/3)
Created By:
Hope Roberts
Date, School & Place:
3/04/2016
George Mason University located in Fairfax, Va.
The creation took place in Mathematica for a class project for Math 493, Math Through 3D Printing.
Background of Riemann Surfaces
Riemann surfaces are named after Bernhard Riemann who was the first to study them.
Riemann surfaces are one way to show multi-valued functions. Showing that an element from the domain can map to multiple places in the codomain. They resemble surface like structures consisting of infinite sheets that are separated by vertical distance. They are configured in the complex plane, which has vectors 1, and i where i is imaginary and these vectors span the complex numbers. All complex numbers match to unique points in the complex plane. (mathworld). Another way to show the multi-valued functions is branch cuts, which is to take lines or line-segments of the multi-valued functions.
Representing a multivalued function is to ascribe not one point but instead infinite points to the domain. The sheets represented by the mappings from the origin and are all interconnected because it is undefined at the origin, which makes the origin, point not a part of the domain. The functions can be oriented in different ways by multiplying by the complex number.
My function used for the Riemann surface was z^(1/3) and the surface was mapped using polar coordinates with the branches of the surface the tubes on top.
The branches also called branch cuts that are on my surface representing where the function is not continuous and is also non differentiable. The branches show when a sheet of the surface connects another sheet of the surface, which can be seen by the changing colors in surface in the mathematica code. As you increased distance in the polar coordinates you continue crossing branch cuts where the sheets are meeting. This is seen in my code and in my print represented by the tube overlay.
The second picture shows the surface without the tube overlay.
The third picture shows the tubes separate.
The fourth shows the combination.
And the final picture shows the stl file loaded onto MakerBot.
Similar models
grabcad
free

Riemann Surface
...dinates you continue crossing "branch cuts" where the sheets are meeting. this can be visible in my 3d rendered images.
thingiverse
free

Riemann Surface by khorstm
...n a neighborhood of the point, may be defined between them. these surfaces were first studied by and named after bernard riemann.
thingiverse
free
Complex Surfaces 3D Object
...ta)
our complex function f is
f(z) = sin(exp(z)^(2/3)), where z = x + iy, so
f(z) = sin(exp(rcos(theta) + ir*sin(theta))^(2/3)).
thingiverse
free

ArcTan Riemann Surface
...b.
this was created for a course at george mason university: math through 3d printing under the instruction of dr. evelyn sander.
thingiverse
free

Riemann Surface in Polar Coordinates by Kristalista
...you get a three-sided shape. this is a process similar to what i did to create this plot from...
thingiverse
free

Boy's surface by quarague
...aw all the edges.
the main file is boys_surface_vertices which gives a rendering of boy's surface using a simple square mesh.
grabcad
free

Rosa Mathematica
... design, i hope to capture some of its beauty.
i included a quote from the u-m printing services to show that it can be printed.
thingiverse
free

Multibrot Set by susan_tarabulsi
...essfully printing this object.
references:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/multibrot_sethttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/mandelbrot_set
thingiverse
free

Sombrero surface by osj1961
...e^{-kr}*cos(r) is rendered here in a smooth version, two different 2d riemann sums and a model showing the contours/level curves.
thingiverse
free

Inverted Horn: z = x^(1/4) + y^(1/4) by jamesford007
...surface has a different name, but i call it an inverted horn. it actually has a pretty sharp point, so watch out enemies of math!
Riemann
thingiverse
free
Riemann Sums by deisterhold
...riemann sums by deisterhold
thingiverse
left, right, and mid-point riemann sums
thingiverse
free

Riemann Surface by khorstm
...n a neighborhood of the point, may be defined between them. these surfaces were first studied by and named after bernard riemann.
thingiverse
free

Riemann Surface on Exponent
... cylinder is simple it is not simply done in code since it is normally worked in imaginary field so has to be added post riemann.
thingiverse
free

2-D Riemann sums by osj1961
... 3xy^2. the number of divisions and the particular function shown can easily be changed in the top section of the openscad file.
thingiverse
free

ArcTan Riemann Surface
...b.
this was created for a course at george mason university: math through 3d printing under the instruction of dr. evelyn sander.
thingiverse
free

Riemann Surface in Polar Coordinates by Kristalista
...[1] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4mmszralqkc&list=pliahhy2ibx9g6kivz_703g3kjxapkknaf&index=13&ab_channel=welchlabs
thingiverse
free

Fractional Derivative Graph of an Exponential Function by kahrendt
...dimensional graph of e^x, with one axis representing the riemannliouville fractional derivative order ranging from 0 to 1. the...
thingiverse
free

Sombrero surface by osj1961
...rendered here in a smooth version, two different 2d riemann sums and a model showing the contours/level...
thingiverse
free

Volume by 16 French Fries by dennedesigns
...z=16-x^2-2y^2 and above the square [0,2]x[0,2] with a double riemann sum. we take the [0,2]x[0,2] square and subdivide it...
R
3ddd
$1

ORLANDO R
...orlando r
3ddd
новый стиль
новый стиль - orlando r
design_connected
$11

R-Table
...r-table
designconnected
henge r-table computer generated 3d model. designed by castagna, massimo.
design_connected
$7

Cone R
...cone r
designconnected
bonaldo cone r computer generated 3d model. designed by pasini, ennio.
3ddd
$1

R&B
...r&b
3ddd
r&b
спальный гарнитур r&b;
3d_export
$5

nissan gt-r
...nissan gt-r
3dexport
this is nissan gt-r
turbosquid
$10

R for ROBOT
...osquid
royalty free 3d model r for robot for download as max on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1694233)
turbosquid
$5

Letter r
...urbosquid
royalty free 3d model letter r for download as max on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1408525)
turbosquid
$5

Letter R
...urbosquid
royalty free 3d model letter r for download as max on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1408526)
3d_export
$5
react r
...r 9 lamps (6+3) ø 60 × 21 cm 12 lamps (9+3) ø 80 × 21 cm polys: 208 539 verts: 213 675 https://ru.lampachn.com/react-r-p0551.html
turbosquid
$40

R-73
...uid
royalty free 3d model r-73 for download as blend and fbx on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1620664)
Surface
design_connected
$9

Surface
...surface
designconnected
rosenthal surface computer generated 3d model.
3d_export
$18

surface-cracked surface 27
...surface 27
3dexport
surface-cracked surface 27<br>max 2015 v-ray 3 max 2015<br>textures<br>all files in zip...
3d_export
$18

surface-cracked surface 27
...surface 27
3dexport
surface-cracked surface 27<br>max 2015 v-ray 3 max 2015<br>textures<br>all files in zip...
3d_export
$5

surface base
...surface base
3dexport
surface base
3ddd
$1

vibia fold surface
...vibia fold surface
3ddd
vibia fold surface , vibia
vibia fold surface
3d_export
$18

surface-yellow river dam-horizontal surface 03
...surface-yellow river dam-horizontal surface 03
3dexport
surface-yellow river dam-horizontal surface 03<br>3ds max 2015
3d_export
$18

surface-yellow river dam-horizontal surface 01
...surface-yellow river dam-horizontal surface 01
3dexport
surface-yellow river dam-horizontal surface 01<br>3ds max 2015
3d_export
$10

surface book 2
...surface book 2
3dexport
surface book 2 laptop
3ddd
$1

Modular Kurk Surface
...modular kurk surface
3ddd
modular
modular kurk surface
turbosquid
$38
Barrier Surface
...ree 3d model barrier surface for download as ma, obj, and fbx on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1233275)
3
turbosquid
$10

Mountain Bike 3 -3 of 3
...model mountain bike 3 (#3 of 3) for download as fbx and blend on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1438752)
turbosquid
$6

Rock 3-3
...urbosquid
royalty free 3d model rock 3-3 for download as obj on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1628065)
turbosquid
$29

Books 150 pieces 3-3-3
...books 150 pieces 3-3-3 for download as max, obj, fbx, and stl on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1384033)
turbosquid
$3

Genesis 3 Clothing 3
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
3d_export
$5

hinge 3
...hinge 3
3dexport
hinge 3
3ddd
$1

Розетка 3
...розетка 3
3ddd
розетка
розетка 3
turbosquid
$50

is-3
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
turbosquid
$10

Mountain Bike 3 -2 of 3
...model mountain bike 3 (#2 of 3) for download as fbx and blend on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1438750)
turbosquid
$10

Mountain Bike 1 -3 of 3
...model mountain bike 1 (#3 of 3) for download as fbx and blend on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1438743)
3d_export
$5

3 CATS
...3 cats
3dexport
3 cats pen holder
1
turbosquid
$69

armchairs(1)(1)
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
turbosquid
$15

ring 1+1
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
turbosquid
$10

chair(1)(1)
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
turbosquid
$8

Chair(1)(1)
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
turbosquid
$2

RING 1(1)
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
turbosquid
$1

house 1(1)
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
turbosquid
$1

Table 1(1)
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
turbosquid
$59

Formula 1(1)
...lty free 3d model formula 1 for download as max, fbx, and obj on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1567088)
design_connected
$11

No 1
...no 1
designconnected
sibast no 1 computer generated 3d model. designed by sibast, helge.
turbosquid
$2

desert house(1)(1)
...3d model desert house(1)(1) for download as 3ds, max, and obj on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1055095)

