3DWarehouse
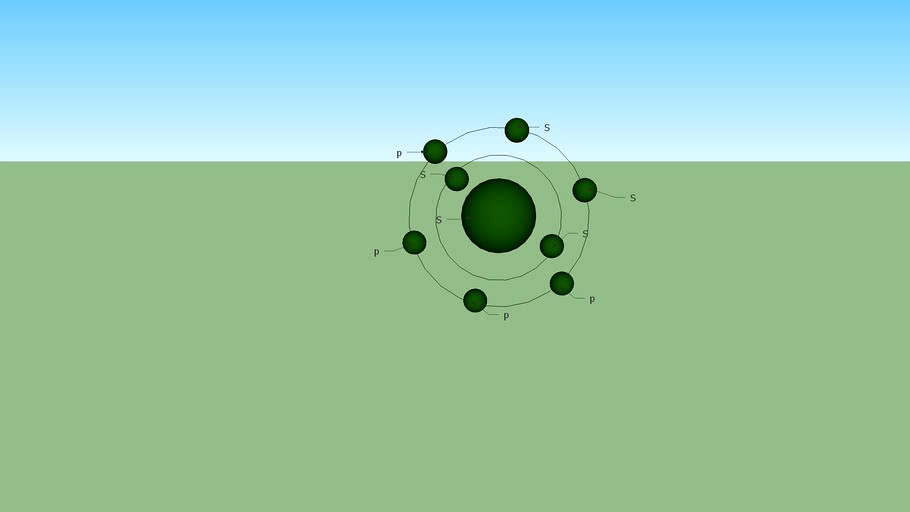
O - Oxygen
by 3DWarehouse
Last crawled date: 1 year, 10 months ago
Electronic configuration Oxygen is a chemical element of the periodic table of the elements. It has a symbol O, such as atomic number 8 and mass number 16. It is part of group 16 elements on the periodic table and is a highly reactive and oxidizing non-metallic agent that easily forms oxides with most elements as well as other compounds. By mass, oxygen is the third most abundant element of the universe, after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two elemental atoms are bound to form a dioxide, a colorless and odorless gas with a chemical formula O2, which constitutes 20.8% of the Earth's atmosphere. It is also the most common chemical element of the earth's crust representing about 47% of the mass (linked to other elements). Dioxide is used in cell respiration and many of the major classes of organic molecules present in living organisms such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids, contain oxygen. Most of the mass of living organisms contains oxygen as a component of water. In contrast, oxygen is constantly restored by photosynthesis of plants, which uses solar energy to produce it from water and carbon dioxide. Oxygen is chemically too reactive to remain a free element in the air. Another form (allotropy) of oxygen is ozone (O3), a gas capable of absorbing ultraviolet radiation considerably and the high-altitude ozone layer helps to protect the biosphere from these radiation. However, near the Earth's surface, ozone is considered a pollutant and is a byproduct of smog. Oxygen was discovered irrespective of Carl Wilhelm Scheele, Uppsala in 1773, and Joseph Priestley in Wiltshire in 1774, but Priestley is often accredited to be the first one because his studies were published earlier than those of Scheele. The name 'oxygen' was coined in 1777 by Antoine Lavoisier, whose experiments with it contributed to discredit the then popular flogistic theory of combustion and corrosion. The name comes from the Greek ὀξύς, oxýs, 'acid' (literally: 'pointed') and the root γεν-, ghen-, meaning 'generating'. This is because at the time of denomination it was mistakenly assumed that all acids required oxygen in their composition. Oxygen is commonly used for residential heating, for internal combustion engines, for the production of steel, plastic, brazing, welding and cutting of certain metals, as a propellant for rockets, Oxygen therapy and the vital support system for aircraft, submarines, spacecraft and to enable underwater activities. #O8 #Oxygen
Similar models
3dwarehouse
free

Si - Silicon
...icon containing compounds, oxygen and metals). silicon is the main component of glass, cement, ceramics and silicon. #si #silicon
thingiverse
free

Oxygen by WillandMrData2
... gas; constitutes 21 percent of the atmosphere by volume; the most abundant element in the earth's crust. o, atomic number 8.
3dwarehouse
free

Na - Sodium
...s highly reactive, burns with a yellow flame, oxidizes in contact with the air and reacts violently with water. #na #na11 #sodium
3dwarehouse
free

Zn - Zinc
...only zinc oxidation state is +2. it has characteristics similar to football, but a lesser reactivity. in the presence...
3dwarehouse
free
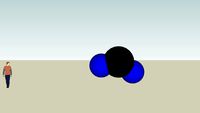
CO2
...co2
3dwarehouse
a carbon dioxide (co2) molecule. #atom #bonding #carbon #chemical #dioxide #molecule #oxygen
3dwarehouse
free

Ac - Actinium
...the series of the actinoids, a group of 15 similar elements of the periodic table between the actinium and...
thingiverse
free

periodic table by cyberguy
...atomic number, usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure (and hence similar chemical properties) appear in...
3dwarehouse
free
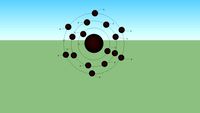
S - Sulfur
...fies soils and water resources, causing serious damage to the natural environment of many industrialized regions. #s #s16 #sulfur
3dwarehouse
free
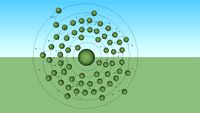
Pm - Promethium
... elements. the promethium shows only a stable oxidation state of +3; however, some +2 composites may exist. #pm #pm61 #promethium
3dwarehouse
free

Ar - Argon
...ble gas of period 3 and constitutes approximately 0.94% of the earth's atmosphere. #ar #argon #electronic_configuration_argon
Oxygen
archibase_planet
free

Oxygen tank
...ygen tank oxygen cylinder oxygen storage oxygen
oxygen tank n080615 - 3d model (*.gsm+*.3ds+*.max) for interior 3d visualization.
turbosquid
$23

Oxygene
...turbosquid
royalty free 3d model oxygene for download as fbx on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1501492)
3d_export
$5

Oxygen tank
...oxygen tank
3dexport
oxygen tank
archive3d
free

Oxygen tank 3D Model
...torage oxygen
oxygen tank n080615 - 3d model (*.gsm+*.3ds+*.max) for interior 3d visualization.
turbosquid
$2

Oxygen Tank
...royalty free 3d model oxygen tank for download as obj and fbx on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1174416)
turbosquid
free

Oxygen Cylinder
...lty free 3d model oxygen cylinder for download as fbx and obj on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1637893)
3d_ocean
$12

oxygen cylinder
...ical object ocean oxygen pressure recreational regulator research science silver steel tank valve
3d oxygen cylinder and material
turbosquid
$18

Oxygen bottle
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
turbosquid
$12

Oxygen Tanks
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
turbosquid
$3

oxygen container
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
O
design_connected
$13

O Tables
...o tables
designconnected
oxdenmarq o tables computer generated 3d model. designed by marquart, dennis.
design_connected
$11

O Bench
...o bench
designconnected
robert kuo o bench computer generated 3d model. designed by kuo, robert.
design_connected
$9

Doble O
...doble o
designconnected
nomon doble o computer generated 3d model. designed by reina, josé maría.
design_connected
$11

O-Nest
...o-nest
designconnected
moroso o-nest seating objects computer generated 3d model. designed by tord boontje.
turbosquid
$2

skillet casseroles o sarten o caserola
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
3ddd
$1

Foscarini O-Space
...foscarini o-space
3ddd
foscarini , o-space
o-space, suspension
design luca nichetto
turbosquid
$20

Ring O
...
turbosquid
royalty free 3d model ring o for download as stl on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1353794)
turbosquid
$5

Letter O
...urbosquid
royalty free 3d model letter o for download as max on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1408519)
turbosquid
$5

Letter O
...urbosquid
royalty free 3d model letter o for download as max on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1408496)
turbosquid
$5

Letter o
...urbosquid
royalty free 3d model letter o for download as max on turbosquid: 3d models for games, architecture, videos. (1408493)
