Thingiverse

GO-GO AirBoat by macakcat
by Thingiverse
Last crawled date: 2 years, 11 months ago
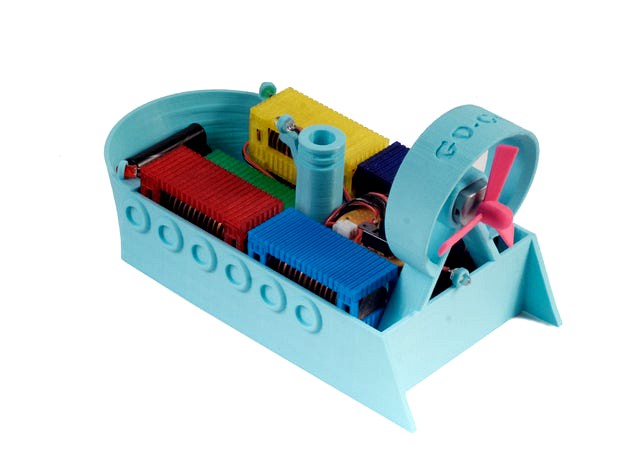
GO-GO AirBoat is a physics concepts and electronics learning kit.
GO-GO AirBoat is a payload-sensing, motorized, propeller airboat.
When GO-GO AirBoat reaches full capacity, watch the motor rev to life, spinning the propeller, and watch GO-GO go! How many pennies can you load before GO-GO goes? Will it sink or will it float? Load your lifesavings aboard, and wave "Bon voyage!" to your GO-GO AirBoat!
Load your cargo containers with up to 20 pennies each (US cent tested). The cargo containers are infinitely stackable! GO-GO's cargo bay area can support up to 5 columns of cargo containers. Many combinations of load and weight distribution possible. Experiment!
Provided instructions include derivation of the "Maximum Number of Pennies" equation to stay afloat with your chosen cargo configuration.
Simple to print! There are only four STL files needed to construct your GO-GO AirBoat and cargo containers so it's easy to do.
GO-GO AirBoat senses when to embark on its long haul across the sea when it is fully loaded to capacity with its valuable cargo. A floating piston inside the boat's smokestack is free to move with the water level and triggers the motor to drive when a certain depth is achieved. This sensor employs a simple infrared LED, phototransistor, and a Darlington pair transistor amplifier stage for switching of a small DC motor.
The depth-sensor trigger point can be mechanically altered using different, floating piston heights of your own creation.
Gain hands-on experience with resistors, capacitors, diodes, LED's, DC motors, bipolar junction transistors (BJT's), Darlington pair transistors, phototransistors as triggers, circuit board layout, and soldering.
The GO-GO AirBoat features a series of basic, discrete component, electronic constructions to help young engineers and future scientists better visualize electrical components, their wiring, and their roles in electronic circuits. The instructions provide step-by-step calculations and descriptions of how the individual circuits function together as a whole.
Use this model as an activity or introduction to subjects such as weight, mass, displacement, density, buoyancy, and center of gravity. Topics covered within the instructions focus on mass, density, and basic algebra. Logic and reasoning skills are exercised to translate calculated values to the real world.
Please click the Instructions tab for a guided walkthrough covering settings, tips, tricks, explanations, exercises, and prompts for further exploration.
Designed by David Choi
GO-GO AirBoat is a payload-sensing, motorized, propeller airboat.
When GO-GO AirBoat reaches full capacity, watch the motor rev to life, spinning the propeller, and watch GO-GO go! How many pennies can you load before GO-GO goes? Will it sink or will it float? Load your lifesavings aboard, and wave "Bon voyage!" to your GO-GO AirBoat!
Load your cargo containers with up to 20 pennies each (US cent tested). The cargo containers are infinitely stackable! GO-GO's cargo bay area can support up to 5 columns of cargo containers. Many combinations of load and weight distribution possible. Experiment!
Provided instructions include derivation of the "Maximum Number of Pennies" equation to stay afloat with your chosen cargo configuration.
Simple to print! There are only four STL files needed to construct your GO-GO AirBoat and cargo containers so it's easy to do.
GO-GO AirBoat senses when to embark on its long haul across the sea when it is fully loaded to capacity with its valuable cargo. A floating piston inside the boat's smokestack is free to move with the water level and triggers the motor to drive when a certain depth is achieved. This sensor employs a simple infrared LED, phototransistor, and a Darlington pair transistor amplifier stage for switching of a small DC motor.
The depth-sensor trigger point can be mechanically altered using different, floating piston heights of your own creation.
Gain hands-on experience with resistors, capacitors, diodes, LED's, DC motors, bipolar junction transistors (BJT's), Darlington pair transistors, phototransistors as triggers, circuit board layout, and soldering.
The GO-GO AirBoat features a series of basic, discrete component, electronic constructions to help young engineers and future scientists better visualize electrical components, their wiring, and their roles in electronic circuits. The instructions provide step-by-step calculations and descriptions of how the individual circuits function together as a whole.
Use this model as an activity or introduction to subjects such as weight, mass, displacement, density, buoyancy, and center of gravity. Topics covered within the instructions focus on mass, density, and basic algebra. Logic and reasoning skills are exercised to translate calculated values to the real world.
Please click the Instructions tab for a guided walkthrough covering settings, tips, tricks, explanations, exercises, and prompts for further exploration.
Designed by David Choi
Similar models
grabcad
free

Transistores
...transistores
grabcad
transistores npn
transistores pnp
triac´s
mosfets
darlington
3dwarehouse
free

Transistor
...transistor
3dwarehouse
transistor, electronic circuit chip
cg_trader
free

MOSFET Transistor
...small ic chip. ic chips not only contain transistors but also other circuit components such as capacitors, resistors, diodes etc.
cg_trader
free

Lowpoly Electronic Components
...r
the pack contains 20 models of electronic components, fuses, electronic boards, integrated circuits, processor and transistors
thingiverse
free

Floating candle #MakeItFloat by henriquepsantos
...total mass of around 25 g, meaning that, theoretically, we could support a maximum of 125 grams (let's say 100 g to be safe).
grabcad
free

PC817 2-Channel Optocoupler Module
...om the power circuit (for example, relays, motors, etc.) we use optocoupler to remove the power circuit noise on control circuit.
grabcad
free

ULN2803A
...uln2803a
grabcad
uln2803a darlington transistor arrays
grabcad
free

ULM2803
...ulm2803
grabcad
transistors darlington 8sorties npn
3dwarehouse
free

DENSITY
...ensity is the mass of a substance per unit volume of that substance; calculated by dividing the mass of a substance by its volume
3dwarehouse
free

TO-92 package
...age
3dwarehouse
typical for low power transistors... #circuit #component #electronics #npn #pnp #semiconductor #to92 #transistor
Macakcat
thingiverse
free

Scribblebot! by halfluck
...will help smooth the motion. special thanks to @allted @macakcat @dagk @jumekubo for using pieces of their models to...
thingiverse
free
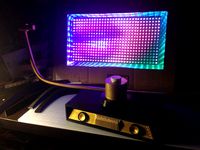
TELEAVIA MATRIX by macakcat
...ng on printing the monitor pieces and will upload pictures when it's done printing! check back soon!
designed by david choi
thingiverse
free

Teknikio Continuity Test Tool by teknikio
...just got a little bit easier. :) designed by macakcat ...
thingiverse
free

Blinky Kitty by teknikio
...sparking sense set to complete this project! designed by macakcat ...
thingiverse
free

Ozobot "Hardwear" Helmet Upgrade Accessory Kit by macakcat
...mets are an expansion to michael parker's classroom exercise for 3d printing with ozobots at dimension learning based in nyc.
thingiverse
free

Wirelessly Powered Tesla Desk Lamp by macakcat
...com/46711/tesla-desk-lamp/
short video and explanation at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ybibn9la6pq
designed by david choi
thingiverse
free

Wirelessly Powered PiBook by macakcat
...watch?v=ylutddiexne
see the wireless circuit in action at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=akxadmjq4q4
designed by david choi
thingiverse
free

Tesla Tower by macakcat
... mudrak. i've only sliced it in half and added a smooth cupola to go with it.
please read the instructions before printing!
thingiverse
free

Mini Wirelessly Powered Tesla Desk Lamp by macakcat
...
resonant frequency: 6.5mhz
spiral inductor: ~0.1uh.
overal dimensions: 2.3" x 2.3" x 3"
designed by david choi
Airboat
cg_studio
$99

Airboat3d model
...odel
cgstudio
.3ds .fbx .lwo .lxo .max .obj - airboat 3d model, royalty free license available, instant download after purchase.
3d_export
$99

Airboat 3D Model
...verglades louisiana engine motor fan fishing recreational alligator bayou propeller
airboat 3d model dzejsi.models 72673 3dexport
3d_export
$10

Electric Boat
...transport of the future. my model is a rubber airboat in the bow part of which there are 3...
turbosquid
$10

AIRBOAT.3DS
... available on turbo squid, the world's leading provider of digital 3d models for visualization, films, television, and games.
thingiverse
free

RC Airboat x4 spilt by FJ_Prints
...hingiverse
i have seen a lot of people asking fore one split into 4 in the comments of the original one . so i decided to do it.
thingiverse
free

Custom Trigger for Flysky FS-GT3B Transmitter by TheMetalikMelon
...could use a 3-channel pistol grip controller for an airboat with an airplane esc. if you have an application...
thingiverse
free

Rc Air boat from floats and 70mm EDF by ultrarc
...edf by ultrarc thingiverse want to make an rc airboat powered by a brushless edf? well if so this...
thingiverse
free

Airboat K280/K200 Fan Duct / Mount by badiozam
...) for the fan itself to mount to this piece.
you'll also need 2x m3x30 or m3x25 screws to fix the mount to the cooling block.
thingiverse
free

RC Airboat by Marwando
...rc airboat by marwando
thingiverse
if you like it support my youtube channel marwando
thanks :)
thingiverse
free

Cheap 3D Printed RC Airboat by 3llogical
...at by 3llogical
thingiverse
frame for 3d printed boat made with eachine e010 drone.
watch video at: https://youtu.be/hh6fah75xym
Go
3ddd
$1

Carpet
...carpet 3ddd ковер go to the tab rendering - effects-hair and fur and...
3d_ocean
$19

AWP Sniper rifle (CS GO)
...ts included: .c4d, .obj – the model contains 42288 polygons – not rigged, scene setup / lighting / environments from the previ...
3ddd
$1
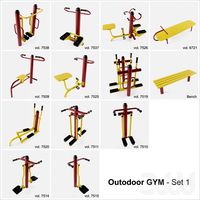
Outdoor Gym Set 1
...change the configuration of the site you need to go in the modifier stack "ground" at the level of...
3ddd
$1

Modern Wall Shelf
...аксессуарами полкиhttp://www.urbanoutfitters.com/urban/catalog/productdetail.jsp?id=26691345&parentid;=a_decorate коробка 1http://www.urbanoutfitters.com/urban/catalog/productdetail.jsp?id=32078453&parentid;=a_decorate коробка 2http://www.urbanoutfitters.com/urban/catalog/productdetail.jsp?id=32078271&parentid;=a_decorate кактусыhttp://www.urbanoutfitters.com/urban/catalog/productdetail.jsp?id=30341077&parentid;=a_decorate мискиhttp://www.urbanoutfitters.com/urban/catalog/productdetail.jsp?id=30332613&parentid;=a_furn_kitchen_eat постер 1http://society6.com/product/gowest-aou_print#1=45 постер 2http://society6.com/product/the-ocean-the-sea-the-wave_print#1=45 украшения...
3ddd
free

Ginger & Jagger Earth To Earth тумба и шкаф
...a way of inspiring creativity. how far would you go for...
3d_ocean
$5

Coffee Cup Take Away (Vray)
...3docean coffee coffee cup coffee cup plastic coffee to go espresso espresso cup interior plastic cup plastic cups plastic...
3d_ocean
$89

Honda CR-V 2010
...model 360 spin: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rual81keaeu a new-look honda cr-v will go on sale in january 2010, with a new diesel...
3d_ocean
$15

Apple iPad Air 2
...in cinema 4d. by purchasing this item you are gong to have: .obj, c4d, .maya, ..e3d, .ae files. clean...
3d_ocean
$5

Cinema 4D Title Preset Holograms Style
...include it. create great designs instantly. just type and go no...
3d_ocean
$14

SET 01 - Bar Stool 5
...it into the scene and you are ready to go there are...
